What Kind of Life Awaits Croatian Anti-Vaxxers Who Refuse Vaccination?
December 29, 2020 – The arrival of COVID-19 vaccines in Croatia has been met with much relief by many people. But, not everyone is happy. Conspiracy theorists - those who favour disreputable sources and 'whispers on the wind' to real science - are reticent, some even angry. So, what kind of life awaits Croatian anti-vaxxers who refuse to take the vaccine?
The people who inhabit the lands now known as Croatia have a long history of being pushed around. For this, they cannot be blamed. Greatly outnumbered by the occupying armies of some of the most powerful empires of all time - the Romans, Venetians, Austro-Hungarians and Ottomans - their rebellions against such overlords have been relatively small in number. Their default setting has been to visit the kafana at the end of the day and moan, grumble, gossip - perhaps even plot - against those who make their lives disagreeable.
Croatia was finally freed of its last imposing masters over two decades ago. But, true to form, the grumbling in the kafanas has continued. Except, now that the kafanas are all closed in response to Coronavirus, the moaning has moved almost exclusively to the internet. And, it has reached a shrieking pitch.
The arrival of COVID-19 vaccines in Croatia has been met with much relief by many Croatians. The news of the first vaccinated citizen, followed by the first vaccinated healthcare workers, was also well received. You can tell this from the overwhelmingly large amount of 'likes' such news generates when posted to social media. These warm welcomers of good news in Croatia could be best described as the silent majority. And, in the same way most Croatians lay subdued for lifetimes under bullying empires, this silent, sensible majority is drowned out by the deafening vitriol of the unhinged within the comments sections underneath.
These arch-moaners appear in the comments on most issues, railing against the increasingly modern ways of the world. On the issue of Coronavirus and the incoming vaccines, it is the Croatian anti-vaxxers who are angrily dominating the discourse.
It appears near pointless to debate with them. They are not ones for science, facts nor reasonable debate. Not for them are the reports of scientific journals, the BBC, The New York Times, The Guardian, Al Jazeera, or The Washington Post. Instead, they cite the most spurious of sources – a website nobody else has heard of, a document written by a friendless doctor from the Texas farming community who has a curiously photoshopped profile picture, a Youtube video made for the same price as a hamburger and narrated by a 17-year-old from the outside toilet. There's no point telling them that the vaccines coming onto the market were actually designed back on January 13, just two days after the Coronavirus genetic sequence had been made public and that it has taken until now to produce them, due to stringent testing on their safety. No. Because for Croatian anti-vaxxers, whispers on the wind, the horoscopes, crystal ball of the fortune-teller and the inescapable stare of Braco are just as reliable - if they're telling you what you want to believe. For whichever lunatic theory you want to adopt, you can look online and you'll be sure to find some crackpot to back it up. The internet is the great leveller for Croatian anti-vaxxers as well as everywhere else - a place where deposed Nigerian royalty who want to put money in your bank account have just as much credence as an 80-year-old media title with a blemishless reputation.
Of course, while life is too short to even debate with anti-vaxxers in Croatia or anywhere else, that's not to say they are undeserving of sympathy. In our recent interview with a doctor working on the Coronavirus frontline in a Croatian hospital, they generously raised an interesting defence of the tin-foil hat brigade - “It's not always the content of the conspiracy theory that appeals to these people as much as it is their inability to accept facts – the truth – because they have little faith in the authorities that are telling them.”
Finding fault in authorities is far from unique to Croatia. Yes, there is a certain amount of kafana moaning and grumbling all over the world, and often for good reason. Politicians are more than aware of this. And, in an era of widespread voter apathy and low voter turnout, where yet another silent majority has the potential so easily to change the names of those who govern, this is exactly why politicians will abstain from making the Coronavirus vaccines mandatory. With things as they currently stand, it is near inconceivable that Coronavirus vaccines will be made compulsory in Croatia or in any other western democracy. Good news for Croatian anti-vaxxers? Well, not quite, because it is highly likely that the private sector will be among the greatest of persuaders for vaccination. It is not unthinkable that we are about to enter a wholly new two-tiered society – the vaccinated and the unvaccinated. And signs of what that life might look like for Croatian anti-vaxxers are not good. They are not good at all.
“Vaccination could become one of the measures that would make it possible to come to events,” Stefan Breitenmoser, general manager of the Professional Association of Swiss Organizers of Concerts, Events and Festivals, told Sonntags Blick in the past week. In Switzerland, vaccination began on Wednesday and it is free. It is not only the entertainment events industry that is considering the measure - the Swiss Football League similarly said it is giving it serious consideration. Professional sports and the events industry have lost billions during the pandemic. The 2021 Olympics hangs on a knife-edge in regards to accepting audiences into its stadiums – it has already been delayed by a year. It is highly conceivable that access to all large events in future will be dependent on proof of vaccination.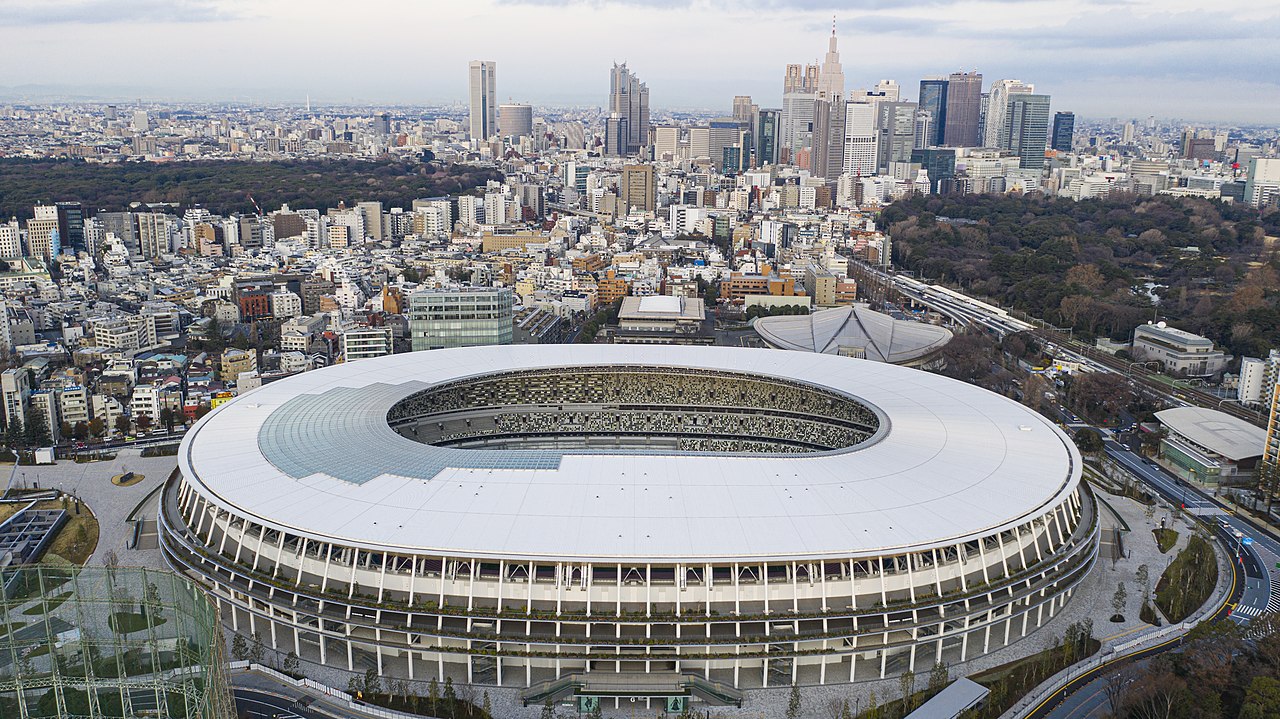 The National Stadium in Japan was due to host some of the key events of the 2020 Summer Olympics. The whole event has been delayed until summer 2021, in response to the pandemic © Arne Müseler
The National Stadium in Japan was due to host some of the key events of the 2020 Summer Olympics. The whole event has been delayed until summer 2021, in response to the pandemic © Arne Müseler
In an interview on N1 television in Croatia over recent days, epidemiologist Branko Kolarić - a member of the Scientific Council of the Government of the Republic of Croatia - echoed similar thinking. He stated that a list of the vaccinated will be carefully maintained, most likely through some kind of e-documents, and although vaccination will not be mandatory, vaccination will bring some benefits - such as air travel, group gatherings and attendance of concerts and festivals. You are surely not going to see police or soldiers checking your vaccination status at the entry to a dance music festival in Dalmatia. But, it is highly likely that event organisers will insist on proof of vaccination before granting entry. Even if they don't wish to, it is more than conceivable that they would not be granted the necessary licenses nor insurance without assuming such a position.
Another industry that has lost billions in the pandemic is the travel and tourism sector. Little surprise then to have found budget airline Ryanair launching a new campaign of 'Jab and go' over the last few days. The suggestion is crystal clear – get vaccinated, you can come on our planes, we'll allow you to travel. Ryanair will certainly not be the last airline to assume responsibility for vetting passengers' vaccination status. Croatian anti-vaxxers had better be really happy to be here, because international borders may well be permanently closed for them while they remain unvaccinated.
So, a life with no spectating at big sports events, no more large concerts or music festivals and no more international travel is what seems to be just around the corner for Croatian anti-vaxxers. Sounds harsh, unpleasant. But what if it extends to libraries, schools or even hospitals? We don't yet know anything concrete about the lower tier of existence Croatian anti-vaxxers may choose to dwell in. But, it's not where I want to live. Perhaps they'll even be forced to drink exclusively in their own anti-vaxxer kafanas? For sure they'll be easy to identify – they'll be the ones from which the loudest moans are coming.
The views expressed in this article are solely those of the author and are not necessarily shared by Total Croatia News
Croatian Healthcare Workers: Christmas's Forgotten Heroes?
December 28, 2020 – Amidst the difficulties of a second lockdown, a socially distanced Christmas and yet more earthquakes, have we forgotten about Croatian healthcare workers? TCN decided to interview a doctor working on the front line of the fight against COVID
During the first lockdown, it was all about the balconies. Saxophonists, DJs, opera singers – we were entertained on social media by a string of balcony-based stunts that somehow showed resilience, community spirit, humour. Zagreb was no exception. A trend of clapping on balconies in appreciation of healthcare workers passed from country to country and was picked up in Zagreb. After the applause finished, people went back inside. Nothing much had changed. It was a nice enough gesture.
Since the start of summer, no such applause has been heard. Perhaps the release from lockdown gave the signal that the lives of Croatian healthcare workers had also become much easier? That certainly wasn't the case. Though the number of people infected with COVID has grown significantly over recent weeks, Croatian healthcare workers have been treating people sick with COVID since springtime.
Croatian healthcare workers are currently busier with COVID patients than at any time before. And yet, there are no more trips out onto the balconies to show our appreciation for them. Perhaps it's now too cold outside? Perhaps some aren't aware how busy Croatian healthcare workers currently are with COVID patients? Are we perhaps guilty of taking Croatian healthcare workers for granted? Or, maybe we have simply put Croatian healthcare workers to the back of our minds as we struggle with our own challenges?
Throughout this year, TCN has been pleased to report many instances of generosity and innovation directed towards the fight against COVID. Certainly, not everyone in the country is guilty of forgetting about the Croatian healthcare workers who are on the front line fighting this disease. But, how much impact do these instances have on the general lives of Croatian healthcare workers? What is it like to no longer hear the nightly appreciation from our balconies? And, just what is life like as one of the many Croatian healthcare workers battling COVID in the year of the pandemic? TCN decided to interview one to find out.
The doctor we spoke with is a resident physician, working at a smaller community hospital in the continental part of Croatia. They agreed to speak with us on the condition that they do so anonymously.
Looking back at the first lockdown, we didn't know so much about COVID back then. We didn't know exactly how it was spread, the different manifestations of the disease, what course the disease took, nor what the recovery could be like. I think the government did a really good job of responding to the threat as they saw it. We had a small spike in cases, but that is minuscule to what we have now.
I think people generally did what they were told because they thought it would be temporary and they could see the sense in starving the disease out.
At the hospital, we were at first caught a little off guard with the amount of PPE we had and some other resources that we needed. For ICU and ventilators, we were well equipped.
Some of the residents were given some paid leave. It was important to put human resources into tiers. Croatian healthcare workers were certainly more predisposed to catching the disease, simply because they were around it every day.
After such great early successes, I was surprised that everything was relaxed later on to allow the tourist season to take place how it did, and for events like the Vukovar commemoration. It felt like it was a calculated risk. The lockdown we are now in is perhaps too little, too late. The disease is out there now, wild. The numbers of infected people are significantly higher.
The difficulty with this disease is that people can be infected and have very few or no symptoms at all. They might not know they are spreading the virus. You might not know you're sitting next to someone who has it.
Even though we're not at the centre of care for a major population area or city, we saw cases of the disease almost immediately. Our community hospital services an area containing around 150, 000 people. The first cases in April came from nursing homes – elderly, vulnerable people, many with pre-existing conditions. We were well equipped to handle it. Now, we are stretched on a daily basis. We fill the beds with sick people as soon as we empty them.
We wear masks and PPE all day, all the time. All Croatian healthcare workers in hospitals currently do this. Every patient who comes in, regardless of their symptoms, we treat them as though they are carrying the disease.
A lot of residents like me, who are working towards getting their specialty, go to do some periods of work in larger hospitals in the bigger cities. Now, many of those residents have been called back to their community hospitals – we are short on human resources.
The hospital has had to restructure itself significantly. Lots of doctors have been asked to provide cover in the emergency department. Over half of that area is now fully dedicated to COVID.
What do COVID patients look like in regards to their symptoms? It depends on their age and risk group, but you see people who look like they have flu or bacterial pneumonia, you see people who are in acute respiratory distress. Sometimes they have neurological changes, some of them look like they have had a stroke. Some people who have been infected and have supposedly got over the worst of the symptoms, come back in after a month or two with blood clotting problems – blood clots in the legs, which have a tendency to travel up to the lungs and cause a pulmonary embolism. That's a pretty big medical emergency. Some who have pre-existing heart conditions come in with a heart attack triggered by them catching COVID – it's more complicated trying to revive someone when you know they have COVID. The presentation of the disease is so variable.
It's not only older people. I've seen young people be admitted with serious reactions to COVID - young, healthy people who have no pre-existing conditions. I've seen young people come in with mild symptoms, they are sent home with antibiotics and steroids. That is the standard treatment – antibiotics to prevent a bacterial super-infection and steroids to prevent an acute reaction by the body's immune system to COVID. - that's what can cause big problems later on, in the course of the illness. But, sometimes that's not enough. I had a young patient just last week - super healthy, worked out regularly, no pre-existing conditions – and his lungs just looked awful. He had to go to the ICU immediately (sadly, this patient later died). That's like no disease I've ever seen before. Really, COVID is a completely new kind of animal.
The new strain of COVID? There is evidence that it can be spread more easily, and that it can affect more younger people, but there is no evidence that it is any more severe. The vaccines will work against it.
We're short on ventilators now. Really, we need two free ventilators at any time, in case there is an emergency admission. We are not currently in the position where we always have two free ventilators – sometimes they are all in use. That's a worry. I worked one shift where the anaesthesiologist said “We just don't have any more space for them – we will just have to put them in the hallway”. I've never seen that before.
I've heard of Croatian healthcare workers, colleagues in other hospitals getting sick with COVID and the hospital asks them to prove they got sick at work. It's pretty clear that's the most likely place they would have got sick because they're working with COVID patients. They were forced to be off work, but only on a lower level of sick pay. If you get ill because of being at work, you get full pay. But, they couldn't prove it, so they didn't get that.
I've been lucky – I haven't caught COVID yet. Well, as far as I know. My pay hasn't gone down, it's gone up – but only because I'm working so many double shifts. I volunteer to provide cover when other members of staff get sick. The specialists – the consultant doctors – they have it worse than us resident doctors. They are more responsible, so they are expected to work more hours. Nobody is pressured or threatened into picking up extra shifts, it's just something that almost all of us just do.
I've read some nice stories about fundraising efforts and donations to Croatian healthcare workers and hospitals in different parts of the country. Everything is appreciated. But, I personally haven't seen any effect of that on our day to day lives at work. Not at our hospital. Maybe there were PPE donations or cash donations, but it hasn't impacted the daily lives of me and the Croatian healthcare workers who are my colleagues. I think I heard that a local garage was giving free cups of coffee if you show your medical ID. Every little is appreciated.
For me and the Croatian healthcare workers who are my colleagues, instead of any kind of personal discounts or donations to staff, we would much prefer if people just took this disease more seriously. Things look very different when you work in a hospital compared to someone outside who maybe doesn't know anyone who got sick.
I came off a particularly difficult double shift a couple of months ago – it was just non-stop COVID admissions, some severe cases. As I was walking home, I walked past a bar that's near to the hospital. They had signs on the walls telling people to keep their distance. But, the bar was absolutely packed – full of young people. It just felt so disappointing. I couldn't help but think of the older relatives they would come in contact with, some who might get really sick.
Instead of people clapping on balconies, I think Croatian healthcare workers would just prefer more general vigilance and personal responsibility – wear your mask, wash your hands regularly, no more parties in the basement. Clapping on balconies is a nice gesture, but ultimately it's an empty one.
How does it feel to know that there are some people out there, in every country, all around the world, who believe COVID is a hoax, or a plot, or not so serious, or that the vaccine is dangerous or something other than what it is?
Well, it's not always the content of the conspiracy theory that appeals to these people as much as it is their inability to accept facts – the truth – because they have little faith in the authorities that are telling them this. Here in Croatia, I think that distrust is quite high – a lot of people are disillusioned with the state and politics, because of corruption. Sometimes over 50% of the population choose not to vote. The dissemination of misinformation over social media doesn't help - if that's where people get their news from. If you look at that example from your own country, where strict measures about movement were put in place by your government, and immediately afterward, the Chief Advisor to the Prime Minister, was caught breaking them to travel across the country with his family to a second home in the countryside, going out on day trips. And he was defended by his colleagues after he was found out! When people see those kinds of things happening, the distrust between people and the authorities just grows.
All of the images in this article are used as illustrations only. None of the places or people depicted are in Croatia or Croatian, except for the first image, a panorama of Zagreb
Nenad Bakic: Why Has the Virus Become So Deadly in the New EU Countries?
December 20, 2020 – The European Union has so far recorded over 300,000 deaths caused by the coronavirus pandemic, with the second wave being 50 percent more deadly than the first one. It is easily possible that the total number will exceed half a million by the time the pandemic is brought under control. Mathematician, investor, and analyst Nenad Bakic explains why for Index.hr.
In terms of the number of deaths per million inhabitants, the new members of the European Union, the countries of the "new European Union", namely the former socialist countries – including, unfortunately, Croatia – are in the lead. Some of them have several tens of times more deaths in the second wave than in the first.
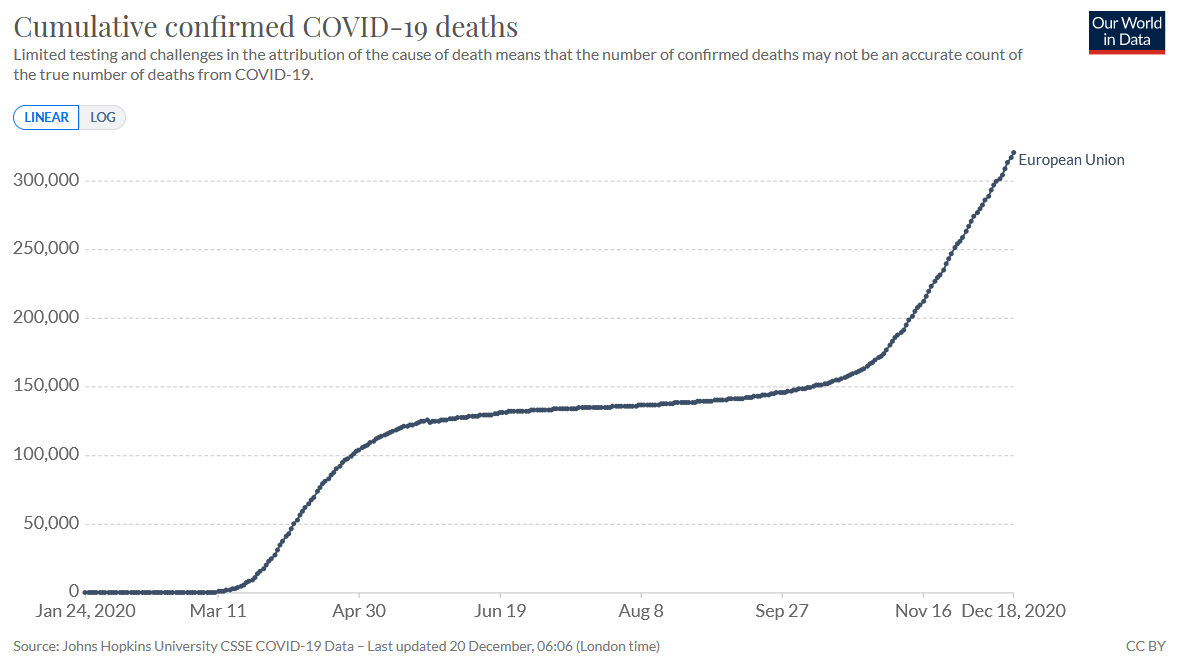
Confirmed cases of death due to coronavirus in the European Union / Source: ourworldindata.org
What is happening? Why did the virus in the second wave become so deadly in the new European Union members? By studying this example, we can learn a lot about the pandemic in general.
- The countries of the New European Union (NE), 11 ex-socialist countries, did very well in the first wave, with only one of them among the 13 most-affected. All the governments of these countries attributed the success to themselves. In some countries like Croatia, it was done by gurus who considered themselves ideologues of barbaric imprisonment or, as they ignorantly called it, "quarantine".
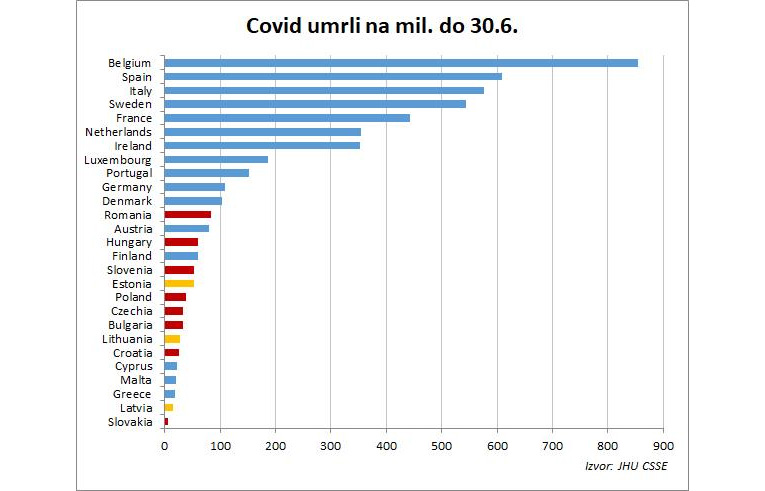
Graph 1. Coronavirus deaths per million, until June 30, 2020. Source: Index.hr / JHU CSSE
They are marked in red on the first graph. A lighter shade highlights the small Baltic countries because something strange is happening there, but it doesn't matter. It is the same when we look at it without this separation.
What is the probability that the NE countries were so much more successful in their will than the older, smarter, and more experienced brothers? Maybe it's something else.
- In the second wave, NE countries were significantly more affected, as we can see in the second graph.
Graph 2. Coronavirus deaths per million, from July 1, 2020 until December 18, 2020. Source: Index.hr / JHU CSSE
Out of the top 8 countries, they occupy seven positions. What is the probability that they are so much more unsuccessful than other countries by their own will? Very small.
Of course, it's easy to recognize a "return to the core value" here – as the virus does what it wants, most countries end up converging to a similar number of deaths. Graph 3 shows the coefficient of variation, which is the standard measure of a set's scatter.
Graph 3. Coefficient of variation, deaths from coronavirus in EU countries per million. Source: Index.hr
Here we can already conclude that the performance of the NE countries as a group has nothing to do with their governments' competencies. The probability that a group with its ability is far above average and then that same group is far below average, especially in a situation like this where the virus spreads across the continent without knowing the boundaries, is zero. Of course, some individual countries are better or worse, both in epidemic management and in treatment.
- But things are only now becoming very interesting. The number of deaths in the second wave not only offset the one from the first wave but also shifted it. The NE countries as a group are now considerably worse than the rest, as we can see in Graph 4.
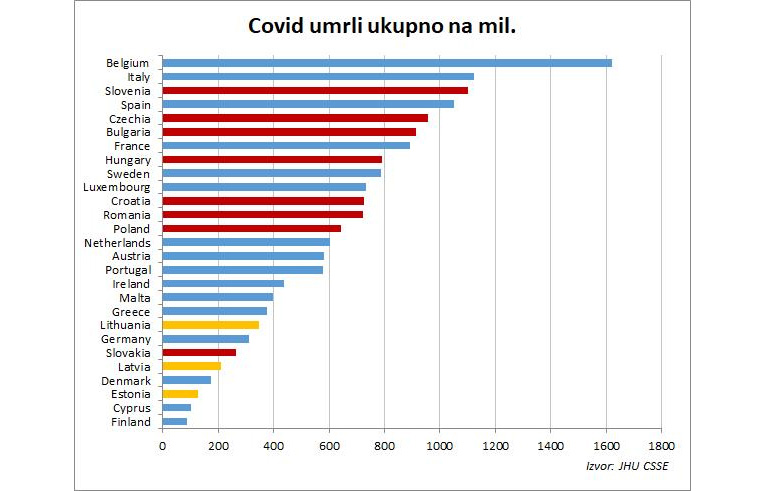
Graph 4. Total coronavirus deaths per million. Source: Index.hr / JHU CSSE
They occupy eight of the first 13 places. If we exclude the small Baltic countries, only Slovakia remains in the lower half, but the situation deteriorates quickly, and it could easily get to the upper half.
As we can see, there is something special about the small Baltic countries and Finland. We still don't know what, and it doesn't matter for this analysis either. If we single out those countries, things become clearer, but the analysis works without them.
- What is the explanation? It can be the following:
- A. It has been shown that COVID-19 is highly seasonal. In NE countries, the epidemic came later in late winter 2020 and therefore could have done much less damage by the time spring came. This is undoubtedly the case with Croatia, as you can see in Graph 5: the reproductive factor R fell below 1 already before the end of March, before the measures were introduced on March 23 in Croatia and could take effect.
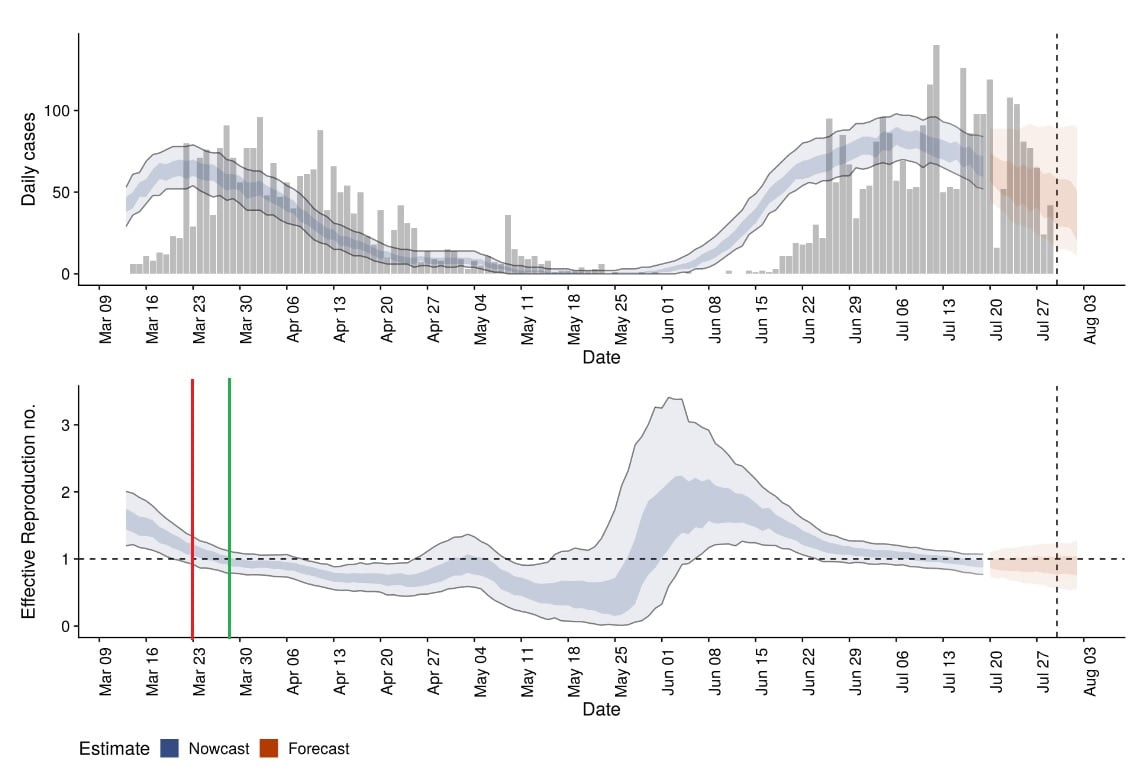
Graph 5. Source: Index.hr
The introduction of a movement prohibition and a drop in R below 1 are marked with a red and green line. An international group of the London School of Health and Tropical Medicine made this calculation, in which a member of the Croatian Scientific Council also participated. Somehow they later forgot to let us know that R had already fallen below 1 even then. However, at the beginning of the epidemic, everything was explained with its help, which advanced countries are doing now. From a time perspective, all of this is now obvious, and that first wave seems completely benign compared to this one now.
But let's remember the psychosis in which we lived then when the concept of "Camp Croatia" with GPS tracking and leaving the house every third or fifth day was already announced when the epidemic was already falling. Inexperienced and impressed by the violent measures, we thought they helped.
But why did the epidemic come later? Here I think the key is in international connectivity. I used an imperfect DHL connectivity index and got a great explanation of the difference, which can be seen in the following chart.
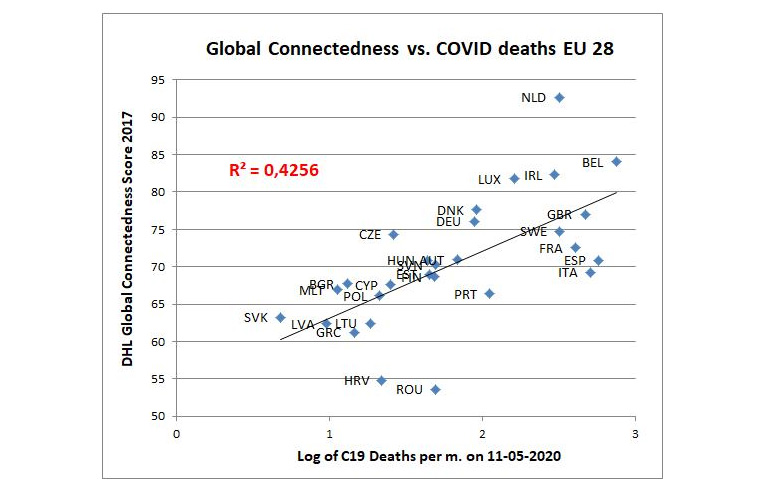
Graph 6. Source: Index.hr
Interestingly, even such an imperfect measure of connectivity explains so much of the variation. As we know, the most affected countries are also the most connected: Italy – densely populated Lombardy and workers from China; Italy, France, Spain – tourism; Belgium – the center of the European Union and others; Sweden – far more connected than its neighbors; and a million Swedes went on school holidays abroad in the last week of February.
- B. The first wave was actually far stronger than it seems now because we tested and hunted cases much less. Many countries found that their dark number (undiscovered cases) was several tens of times higher than those found. In our country, depending on the interpretation of the data, 50 to 80 times, in Denmark 80 (at some point). Now the dark number is probably 5 to 10 in most countries, and the current maybe even just 3 because as more and more people are being tested, and more and more people have been exposed to the virus, the significant dark number has nowhere to hide.
Therefore, most of the countries of old Europe became infected in the spring, a part of the population gained immunity, and significantly more than in the NE, which we cannot see well if we look only at the cases.
- C. It is now quite clear that strongly seasonal is not only an epidemic of SARS-CoV-2 virus but also COVID-19 disease. Clinical pictures are, on average, far more difficult now than a month or two ago. Mortality rates in most EU countries have doubled in just a month or two, meaning twice as many people die among those confirmed infected. It is also the insight of an international group of scientists in which Croatians Gordan Lauc, Alemka Markotić, Dragan Primorac, and others also participated. At first, it was controversial, but now it is generally accepted. Those infected in spring (more in the old than in the NE) had a much better chance of surviving.
- D. One explanation indeed lies in the quality of hospital systems. I believe richer countries have more resources. For example, expensive HFOT devices save lives better than respirators (Croatia has now procured a larger quantity).
- E. Other variables could be considered, such as previous flu seasons, the percentage in the population over 80, or the people in nursing homes. Still, I believe they would indicate a lower expected number of deaths in the NE (but I did not check the data).
In general, the NE countries, including Croatia, were not particularly unprepared for the supposedly expected strong second wave. Let's look at how strength and early outbreak surprised even the most advanced countries, with entirely different strategies: from Germany through Denmark and the Netherlands to Sweden. Remember that in almost all countries, politicians said "let's just wear masks, and we won't need any special measures," then "let's introduce some measures, and we certainly won't need lockdown," and so on. Now we have reached a solid lockdown in almost the entire Union.
Even Germany, the first wave model, is experiencing a real drama after a failed soft lockdown that was supposed to ensure a peaceful Christmas. Denmark and some other countries are already overtaking us in terms of the number of infected. It is not impossible for Germany to overtake us, even in terms of deaths.
In some countries, a third or "second B" wave is already being born, under the influence of winter COVID-19. R is contextual, and even if it falls below 1, under the influence of various circumstances, it can return over 1. It seems that our second wave peak was delayed by merging with that (surprising to all) the third wave.
Conclusion
- The development of the epidemic is mostly beyond the reach of the authorities.
- Countries with stronger measures do not fare better than those with weaker ones. For example, Slovenia is the worst in this group, despite introducing extreme measures before the epidemic escalated.
- The introduced travel ban is not useful. The inspiration for it was the spring ban, which was considered our most important measure, and obviously did not affect the epidemic.
- On the whole, we are not somewhat more unsuccessful than others. Indeed, although some have had significantly stronger measures for longer (this is one group we can compare ourselves to, and the other is our neighborhood shown in Graph 7, and only Serbia is better than us), we should consider any success or failure relatively. It is known that some measures work, such as banning gathering, maintaining physical distance, washing hands, ventilation, etc. The introduction of measures should be proportionate to the goal because the disproportionate introduction of measures has severe negative consequences for society. Countries that introduce brutal and unnecessary measures (there are arguments that some brutal measures even encourage an epidemic) can also cause significant collateral damage to their populations' lives and health.
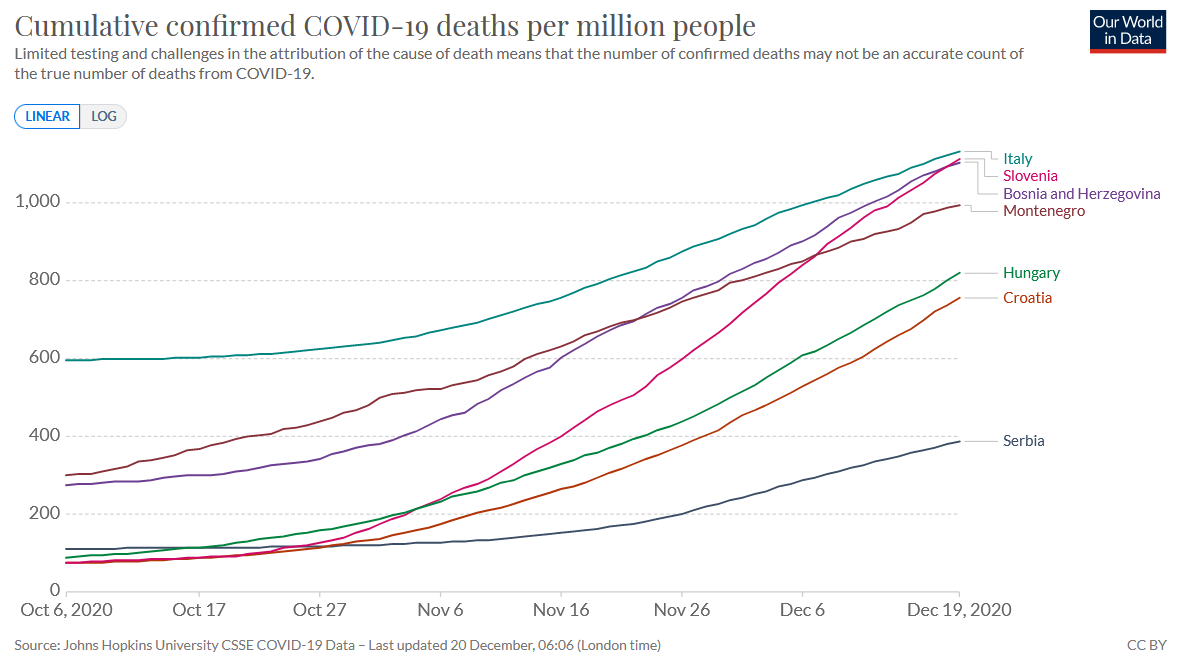
Graph 7. Showing data from October 6, 2020 to December 19, 2020. Source: ourworldindata.org
Let's not forget, the goal in epidemic control is to bring the reproductive factor R below 1, and "zero-covid" strategies have long since been abandoned. Fortunately, in Croatia, R is currently significantly below 1. Let's hope that the data on the epidemic we have are credible and that such a situation will persist.
Of course, the main goal is to save as many lives as possible, although we are often helpless with the virus. Therefore, it is necessary to adhere to epidemiological measures with enhanced protection of vulnerable groups.
To read more about coronavirus in Croatia, read TCN's dedicated page.
Capak: Three-day Rolling Average of COVID-19 Cases Significantly Lower
ZAGREB, Dec 16, 2020 - Croatian Public Health Institute (HZJZ) head Krunoslav Capak said on Wednesday that Croatia this week had a considerably lower three-day rolling average of new COVID-19 cases compared to past weeks and that it was now fifth in the EU when it comes to the number of infections.
At a press conference of the national COVID-19 response team, Capak presented three-day data, according to which there were 7,159 new infections this week, 9,019 new infections last week, while two weeks ago there were 8,269 such cases.
The HZJZ also calculated the cumulative COVID-19 incidence rate for Croatia, which is 43,903 cases per one million inhabitants, and there are four EU countries with higher rates -- Slovenia, Belgium, the Czech Republic, and Luxembourg.
There are still big differences in incidence rates between counties, with Medjimurje County having the highest incidence rate, followed by Varazdin and Krapina-Zagorje counties, while Dubrovnik-Neretva, Istria, and Pozega-Slavonia counties have the lowest incidence.
Capak also said that the decline in the number of new infections had nothing to do with the fact that rapid antigen tests, who had been widely used in the past two weeks, were not included in the statistics, and he explained that rapid antigen tests were not reliable in diagnosing new patients.
He stressed that there was still no reliable information when the COVID-19 vaccine would be registered in the EU, and therefore when it would arrive in Croatia.
"We have a promise from the manufacturer that it will deliver the promised quantities of the vaccine in January. Enough doses of vaccine have been pre-ordered for Croatia's entire population," Capak said.
He explained that it was not yet known how many health workers would be vaccinated because the data from the conducted surveys were not available for all counties.
Asked about the ethics of vaccines, he said there were differences in the technology of vaccine production, but that he personally did not know why some of the vaccines would be unacceptable for ethical reasons.
The head of Zagreb's Dr Fran Mihaljevic hospital for infectious diseases, Alemka Markotic, said that the Oxford and the Russian vaccine had been produced using fetal cells, in the same way, various vaccines had been produced in the past 55 years and which had been used to vaccine millions of people in recent years.
Markotic called on those who had recently got infected with COVID and had risk factors to contact their family doctors or COVID treatment facilities at an early stage of the disease.
Situation with Pandemic Requires National Unity, Says PM
ZAGREB, Dec 16, 2020 - Prime Minister Andrej Plenkovic has said the situation with the pandemic requires national unity, solidarity, and a high degree of responsibility in order to save as many lives as possible and the economy, accusing the opposition of irresponsibly undermining everything that is being done to fight COVID-19.
In an interview with Globus weekly, Plenkovic says new COVID measures are being considered as well as an extension of the ones in force in order to reduce the number of infections.
"I'll reiterate that our priority was and remains to preserve the health of our citizens and save every life. One should clearly say that the choice is not between health and the economy, it is a health and the economy. It would be easiest to introduce another lockdown, but few are asking where the money would come from for salaries and financing the economy."
He says it is extremely important that everyone complies with the COVID measures so as to reduce, through joint efforts, the number of infections and the pressure on hospitals and the medical staff "who are giving their all to save every life and keep the healthcare system running."
Plenkovic says the economy is "key for financing the healthcare system."
Speaking of the arrival of a vaccine, he says that if a large portion of the population gets vaccinated, the infection will disappear sooner.
Announcing a public campaign, he says the wish is for all the information on the vaccine to be transparent, clear and based on science so as to explain to citizens the benefits and how the vaccine can protect them from the disease.
Speaking of the opposition's moves, Plenkovic says it is a pity that their contribution to the COVID crisis "boils down to undermining the work" of the national response team.
"The opposition's attempts to have everything decided in parliament only additionally reveals their deep lack of understanding of the nature of this crisis in which it's necessary to make decisions. How, for example, would a two-thirds majority be achieved in parliament on whether the physical distance should be one meter, a meter and a half or two, how many people can be in shops or on the farmers' market?"
Plenkovic says parliament passed all the laws necessary to enable the government and the COVID response team to make the necessary operational decisions, adding that such a system "has ensured the necessary flexibility for adopting all the necessary measures on short notice."
Plenkovic says the opposition has the right to "irresponsibly undermine all we are doing in the fight against COVID-19, but we will continue to adopt the optimal measures for protecting the health and maintaining the economy."
Croatia Registers 3,327 Infections, 92 Deaths
ZAGREB, Dec 16, 2020 - In the past 24 hours 3,327 coronavirus infections have been registered in Croatia, bringing the number of active cases to 22,042, and 92 COVID-19 patients have died, the national COVID-19 response team said on Wednesday.
Currently, 2,907 patients are hospitalized, including 294 on ventilators, while 53,286 people are self-isolating.
Since the outbreak of the epidemic, Croatia has registered 183,045 coronavirus cases and 2,870 COVID deaths, while 157,773 persons have recovered, including 2,694 in the past 24 hours.
To date, 908,215 persons have been tested for the virus, including 11,387 in the past 24 hours.
Total Lockdown in Croatia Last Possible Option, Says Health Minister Beros
December 13, 2020 - Minister of Health Vili Beros spoke on HRT about a total lockdown in Croatia, the new measures, the current epidemiological situation, and the beginning of vaccination.
Asked if he felt responsible because, according to the European Center for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC), Croatia is the worst in terms of the number of active COVID-19 cases per 100,000 inhabitants, he said:
"Of course, I feel responsible. However, this is a multidimensional, complex crisis, and there are no unambiguous solutions and answers. The only thing that is possible in the given circumstances is to monitor the epidemiological situation from day to day, to monitor all those elements that clearly describe it - the number of newly infected, their distribution, appearance, and based on these elements to prescribe measures," Beros said.
He also added that two weeks is not a big enough period of time to indicate a trend. He also reminded that it took France six weeks after the national lockdown to stabilize the situation. But even after that, they have upward trends again. He believes that four to five weeks should pass after the measures are introduced, assuming that people adhere to them.
He claims that a full lockdown in Croatia is the final option and believes it will not happen.
"We have seen in the example of the neighboring countries what a hard lockdown brings. It is not a good thing. So we need to find a coexistence model in the circumstances of the new normal; we must enable certain economic activities while reducing everything we can reduce. And that is exactly what we are working on; we are trying to balance the measures. It would be easiest to introduce the toughest lockdown and close everything. But that is not realistic, especially since we do not know how long this situation will last," Beros said.
The health minister said that at the moment, it is not very certain that a ban on inter-county travel will be introduced around December 21, although they are discussing it as well. However, this will be introduced if the epidemiological situation is such that it requires a similar way of organizing work.
"Personally, I don't think that will happen. But, if the epidemiological situation is not adequate, we will consider similar measures. Of course, taking into account the working circumstances, i.e., exceptions that would enable work processes," he said.
Emphasizing the importance of antigen tests, Beros said that Croatia procures significant quantities of these tests and will increase their number in hotspots where there are many newly infected.
Stating that the Croatian Institute of Public Health will conduct a national campaign to promote vaccination, Beros warned that - for vaccination to be effective - a large part of the population must be vaccinated. He pointed out that if, for example, less than 70 percent of the population is vaccinated, this will not guarantee significant prevention of the spread of the infection.
Beros also said that introducing a "COVID card" is not being considered at the moment. Still, if the virus continues to cause such severe clinical pictures after spring or summer - that is not ruled out either.
To read more about coronavirus in Croatia, follow TCN's dedicated page.
Google Search Croatia: What Did Croatia Google Search Most in 2020?
December 9, 2020 – It's been a funny old year. Funny as in unusual. Not so much funny haha. The extraordinary nature of the year is reflected in the most-popular Croatia Google search list for 2020, which has just been published. This year's searches hold a stark contrast to last year's.
In 2019, the end-of-year list for Croatia Google search was dominated by results for sporting fixtures, celebrities and entertainment. Although the EU election results and the long-running teacher's strike in Croatia also scored highly in 2019, this year has been dominated by searches of an even more serious and pressing nature.
It will come as no surprise to anyone that the number one Croatia Google search for 2020 was Coronavirus. The global pandemic is likely to top lists all over the world. In this country, its ramifications also created several other high-ranking inclusions on the Croatia Google search list 2020.
Software Google Classroom and Office 365 za škole also feature in the top 10 Croatia Google search list 2020, as parents and students coped with the closure of teaching institutions and prepared to learn and receive lectures online. Another piece of online tech that features in the top 10 was ePropusnica, the travel pass required for inter-regional travel and international travel by car during the various stages of lockdown. If these results are anything to go by, Coronavirus has dominated the lives of Croatians in 2020.
Another big Croatia Google search term in 2020 was Zagreb earthquake. For anyone in Zagreb at the time of the first large tremor, this will also come as little surprise – it was the biggest earthquake experienced for 100 years in Croatia, and it came without warning. Though lasting just a few seconds, there was no reaction more immediate than that of city residents, who ran out into the streets partially clothed. Thousands must have searched the term to find out what was happening, and also after many of the hundreds of aftershocks that have followed.
Here's the list of biggest Croatia Google search terms in 2020
The most-popular Croatia Google search terms in 2020
1. Koronavirus
2. Google Classroom
3. Office 365 za škole
4. Potres Zagreb (Earthquake Zagreb)
5. Kobe Bryant
6. ePropusnica
7. Izbori SAD (US elections)
8. DIP
9. Joe Biden
10. Masoni (Masons)
The most-popular Croatia Google search apps in 2020
1. ePropusnice
2. Zoom
3. Andrija
The most-popular Croatia Google search events in 2020
1. Potres (Earthquake)
2. Izbori SAD (US elections)
3. Izbori (elections)
Aside from the inclusion of the Masons (freemasons), the list is understandable on an international level. It perhaps tells us something about how Croatians use the search engine and how well they respect it as a source for delivering credible information. With Coronavirus vaccines now announced and, all hope, the biggest potential earthquake out of the way, for now, it's understandable for most Croatians to be looking forward to the return of more trivial matters dominating their Google searches in 2021.
17,850 Rapid Antigen Tests Provided for Zagreb Social Welfare Institutions
ZAGREB, Dec 9, 2020 - The City of Zagreb has obtained 17,850 rapid antigen tests for its 60 social welfare institutions, the head of the Zagreb department for social policy, Romana Galic, said on Tuesday.
Of those 60 institutions, 41 are old age homes, and the remaining 19 are institutions for providing care to people with disabilities and other vulnerable groups of citizens, Galic said.
She explained that this had been the first batch of the rapid coronavirus tests which should be used in a period of one month, and the Zagreb authorities hope that they will be provided with additional quantities of those tests.
Testing of staff working in retirement homes and beneficiaries is a manner to prevent the spread of this virus in those institutions, she added.
Currently, there are 196 beneficiaries from 11 old-care homes in Zagreb who are positive for coronavirus. Of them, 22 are receiving hospital treatment, about 50 beneficiaries, who have contracted the virus, are without symptoms and others are with mild symptoms of the COVID-19 disease.
Also, currently, 75 employees from Zagreb's old-age homes are positive for the virus, and an additional 38 are self-isolating.
Galic said that about 75% of beneficiaries in Zagreb's social welfare institutions have said that they are willing to undergo testing, while 36% of the staff have expressed readiness. Also, a marked portion of the staff have recovered from the infection, she said.
Croatia's Coronavirus Update: 4,520 New Cases, 69 Fatalities
ZAGREB, Dec 9, 2020 - In the last 24 hours, out of 12,596 tests performed for coronavirus, 4,520 (36%) have returned positive in Croatia, and 69 people have died of the complications linked to the COVID-19 disease, the national COVID-19 crisis management team reported on Wednesday.
There are now 23,750 active cases, and of the 2,703 are receiving hospital treatment, including 280 patients placed on ventilators, or 23 more than on Tuesday, according to a tally kept by the crisis management team.
Croatia's COVID-related death toll stands at 2,367.
Since February 25, when the first case was confirmed in the country, 159,372 people have been infected with the novel virus. A total of 837,619 people have been tested to date. More than 131,000 have recovered.
Currently, 57835 people are in self-isolation.


