Dijana Zadravec Presents Her Evidence of Corruption in a Zagreb Hospital
ZAGREB, 15 June, 2021 - The National Anti-Corruption Council on Tuesday interviewed the dismissed head of the radiology ward of Zagreb's Sisters of Charity Hospital, Dijana Zadravec, who presented her evidence of criminal activities used to siphon money from the hospital.
Zadravec, who has been on sick leave since May, told members of that parliamentary body that she learned yesterday from the media that acting hospital director Zoran Vatavuk had given her a warning before dismissal for harming the hospital's reputation, noting that the hospital's reputation was harmed by corruption and those who committed and covered it up.
Zadravec said that her fight against corruption started in 2016, when her persecution and harassment started as well.
She said that as the deputy hospital head she reported in 2016 the charging of fictitious overtime work which the then director Mario Zovak had covered up, adding that she had reported this to the prosecutorial authorities and the Health Ministry.
Zadravec said that in late 2020 she discovered a criminal network at the hospital, with public money being siphoned by doctors, which was why she reported them for abuse of office.
The doctor, who claims to have extensive documentation proving her allegations, says that offers to suppliers with whom the hospital did business without public tenders, since the last public tender was conducted in 2019, were signed by doctors Vladimir Kalousek and Branimir Čule, and that the offers exceeded HRK 30 million.
She also cited cases when less material was used for operations than the quantity ordered from suppliers.
Commenting on Zadravec's allegations, the State Secretary and chair of the Sisters of Charity Hospital Steering Board, Tomislav Dulibić, said that hospital documentation was being checked by inspectors from the health and finance ministries and the HZZO health insurance agency.
"According to preliminary information, no significant departures have been found, except for some minor irregularities. Eleven inspectors are working on this, invite them to testify," Dulibić told the Anti-Corruption Council.
He said that the decision to carry out the inspection at the hospital was made a couple of weeks ago, noting that the relevant proceedings were underway.
The chair of the Anti-Corruption Council, Nikola Grmoja, asked if anyone had responded to Zadravec's claims, to which Zadravec said that after she reported the false charging of overtime work, Health Ministry inspectors were called in and concluded that the matter should be investigated by the hospital director.
Allegations should be investigated as soon as possible
After conducting the interviews today, the Anti-Corruption Council adopted a conclusion asking the ministries of health, finances and economy as well as the prosecutorial authorities and the USKOK anti-corruption office to determine facts related to the case as soon as possible.
Zadravec was told to submit copies of the reports she had sent to the competent authorities as well as the text message in which, she claims, Parliament Speaker Gordan Jandroković lobbied for Zovak's reappointment as the hospital head.
The Anti-Corruption Council will send the audio recording of today's hearing to the prosecutorial authorities, and it will ask the Health Ministry to submit all documents on inspections conducted at the hospital since 2016 or explain why no inspections were conducted.
The Council will also ask the government to secure additional conditions for the employment of financial investigators at courts in four big cities.
For more about politics in Croatia, follow TCN's dedicated page.
Croatian Healthcare Workers: Christmas's Forgotten Heroes?
December 28, 2020 – Amidst the difficulties of a second lockdown, a socially distanced Christmas and yet more earthquakes, have we forgotten about Croatian healthcare workers? TCN decided to interview a doctor working on the front line of the fight against COVID
During the first lockdown, it was all about the balconies. Saxophonists, DJs, opera singers – we were entertained on social media by a string of balcony-based stunts that somehow showed resilience, community spirit, humour. Zagreb was no exception. A trend of clapping on balconies in appreciation of healthcare workers passed from country to country and was picked up in Zagreb. After the applause finished, people went back inside. Nothing much had changed. It was a nice enough gesture.
Since the start of summer, no such applause has been heard. Perhaps the release from lockdown gave the signal that the lives of Croatian healthcare workers had also become much easier? That certainly wasn't the case. Though the number of people infected with COVID has grown significantly over recent weeks, Croatian healthcare workers have been treating people sick with COVID since springtime.
Croatian healthcare workers are currently busier with COVID patients than at any time before. And yet, there are no more trips out onto the balconies to show our appreciation for them. Perhaps it's now too cold outside? Perhaps some aren't aware how busy Croatian healthcare workers currently are with COVID patients? Are we perhaps guilty of taking Croatian healthcare workers for granted? Or, maybe we have simply put Croatian healthcare workers to the back of our minds as we struggle with our own challenges?
Throughout this year, TCN has been pleased to report many instances of generosity and innovation directed towards the fight against COVID. Certainly, not everyone in the country is guilty of forgetting about the Croatian healthcare workers who are on the front line fighting this disease. But, how much impact do these instances have on the general lives of Croatian healthcare workers? What is it like to no longer hear the nightly appreciation from our balconies? And, just what is life like as one of the many Croatian healthcare workers battling COVID in the year of the pandemic? TCN decided to interview one to find out.
The doctor we spoke with is a resident physician, working at a smaller community hospital in the continental part of Croatia. They agreed to speak with us on the condition that they do so anonymously.
Looking back at the first lockdown, we didn't know so much about COVID back then. We didn't know exactly how it was spread, the different manifestations of the disease, what course the disease took, nor what the recovery could be like. I think the government did a really good job of responding to the threat as they saw it. We had a small spike in cases, but that is minuscule to what we have now.
I think people generally did what they were told because they thought it would be temporary and they could see the sense in starving the disease out.
At the hospital, we were at first caught a little off guard with the amount of PPE we had and some other resources that we needed. For ICU and ventilators, we were well equipped.
Some of the residents were given some paid leave. It was important to put human resources into tiers. Croatian healthcare workers were certainly more predisposed to catching the disease, simply because they were around it every day.
After such great early successes, I was surprised that everything was relaxed later on to allow the tourist season to take place how it did, and for events like the Vukovar commemoration. It felt like it was a calculated risk. The lockdown we are now in is perhaps too little, too late. The disease is out there now, wild. The numbers of infected people are significantly higher.
The difficulty with this disease is that people can be infected and have very few or no symptoms at all. They might not know they are spreading the virus. You might not know you're sitting next to someone who has it.
Even though we're not at the centre of care for a major population area or city, we saw cases of the disease almost immediately. Our community hospital services an area containing around 150, 000 people. The first cases in April came from nursing homes – elderly, vulnerable people, many with pre-existing conditions. We were well equipped to handle it. Now, we are stretched on a daily basis. We fill the beds with sick people as soon as we empty them.
We wear masks and PPE all day, all the time. All Croatian healthcare workers in hospitals currently do this. Every patient who comes in, regardless of their symptoms, we treat them as though they are carrying the disease.
A lot of residents like me, who are working towards getting their specialty, go to do some periods of work in larger hospitals in the bigger cities. Now, many of those residents have been called back to their community hospitals – we are short on human resources.
The hospital has had to restructure itself significantly. Lots of doctors have been asked to provide cover in the emergency department. Over half of that area is now fully dedicated to COVID.
What do COVID patients look like in regards to their symptoms? It depends on their age and risk group, but you see people who look like they have flu or bacterial pneumonia, you see people who are in acute respiratory distress. Sometimes they have neurological changes, some of them look like they have had a stroke. Some people who have been infected and have supposedly got over the worst of the symptoms, come back in after a month or two with blood clotting problems – blood clots in the legs, which have a tendency to travel up to the lungs and cause a pulmonary embolism. That's a pretty big medical emergency. Some who have pre-existing heart conditions come in with a heart attack triggered by them catching COVID – it's more complicated trying to revive someone when you know they have COVID. The presentation of the disease is so variable.
It's not only older people. I've seen young people be admitted with serious reactions to COVID - young, healthy people who have no pre-existing conditions. I've seen young people come in with mild symptoms, they are sent home with antibiotics and steroids. That is the standard treatment – antibiotics to prevent a bacterial super-infection and steroids to prevent an acute reaction by the body's immune system to COVID. - that's what can cause big problems later on, in the course of the illness. But, sometimes that's not enough. I had a young patient just last week - super healthy, worked out regularly, no pre-existing conditions – and his lungs just looked awful. He had to go to the ICU immediately (sadly, this patient later died). That's like no disease I've ever seen before. Really, COVID is a completely new kind of animal.
The new strain of COVID? There is evidence that it can be spread more easily, and that it can affect more younger people, but there is no evidence that it is any more severe. The vaccines will work against it.
We're short on ventilators now. Really, we need two free ventilators at any time, in case there is an emergency admission. We are not currently in the position where we always have two free ventilators – sometimes they are all in use. That's a worry. I worked one shift where the anaesthesiologist said “We just don't have any more space for them – we will just have to put them in the hallway”. I've never seen that before.
I've heard of Croatian healthcare workers, colleagues in other hospitals getting sick with COVID and the hospital asks them to prove they got sick at work. It's pretty clear that's the most likely place they would have got sick because they're working with COVID patients. They were forced to be off work, but only on a lower level of sick pay. If you get ill because of being at work, you get full pay. But, they couldn't prove it, so they didn't get that.
I've been lucky – I haven't caught COVID yet. Well, as far as I know. My pay hasn't gone down, it's gone up – but only because I'm working so many double shifts. I volunteer to provide cover when other members of staff get sick. The specialists – the consultant doctors – they have it worse than us resident doctors. They are more responsible, so they are expected to work more hours. Nobody is pressured or threatened into picking up extra shifts, it's just something that almost all of us just do.
I've read some nice stories about fundraising efforts and donations to Croatian healthcare workers and hospitals in different parts of the country. Everything is appreciated. But, I personally haven't seen any effect of that on our day to day lives at work. Not at our hospital. Maybe there were PPE donations or cash donations, but it hasn't impacted the daily lives of me and the Croatian healthcare workers who are my colleagues. I think I heard that a local garage was giving free cups of coffee if you show your medical ID. Every little is appreciated.
For me and the Croatian healthcare workers who are my colleagues, instead of any kind of personal discounts or donations to staff, we would much prefer if people just took this disease more seriously. Things look very different when you work in a hospital compared to someone outside who maybe doesn't know anyone who got sick.
I came off a particularly difficult double shift a couple of months ago – it was just non-stop COVID admissions, some severe cases. As I was walking home, I walked past a bar that's near to the hospital. They had signs on the walls telling people to keep their distance. But, the bar was absolutely packed – full of young people. It just felt so disappointing. I couldn't help but think of the older relatives they would come in contact with, some who might get really sick.
Instead of people clapping on balconies, I think Croatian healthcare workers would just prefer more general vigilance and personal responsibility – wear your mask, wash your hands regularly, no more parties in the basement. Clapping on balconies is a nice gesture, but ultimately it's an empty one.
How does it feel to know that there are some people out there, in every country, all around the world, who believe COVID is a hoax, or a plot, or not so serious, or that the vaccine is dangerous or something other than what it is?
Well, it's not always the content of the conspiracy theory that appeals to these people as much as it is their inability to accept facts – the truth – because they have little faith in the authorities that are telling them this. Here in Croatia, I think that distrust is quite high – a lot of people are disillusioned with the state and politics, because of corruption. Sometimes over 50% of the population choose not to vote. The dissemination of misinformation over social media doesn't help - if that's where people get their news from. If you look at that example from your own country, where strict measures about movement were put in place by your government, and immediately afterward, the Chief Advisor to the Prime Minister, was caught breaking them to travel across the country with his family to a second home in the countryside, going out on day trips. And he was defended by his colleagues after he was found out! When people see those kinds of things happening, the distrust between people and the authorities just grows.
All of the images in this article are used as illustrations only. None of the places or people depicted are in Croatia or Croatian, except for the first image, a panorama of Zagreb
Hero Croatian Hospital Does Free Dentistry for All Special Needs Children
Wednesday, 9 September 2020 – Angels in white from heroic Croatian hospital Dr. fra Mato Nikolić in Nova Bila offer free dentistry for all special needs children
Few young people look forward to visiting the dentist. But, imagine how such a visit must be if the world is already a confusing and difficult place for you. These are the difficulties of dentistry for all special needs children.
“Children with special needs suffer from a range of disorders,” Dr. Nikola Matković tells TCN over the phone from Croatian hospital Dr fra Mato Nikolić in Nova Bila, near Vitez, central Bosnia. “They can have stunted mental development, autism, Down's syndrome, disharmonic development, epilepsy, cerebral palsy. They all need to put under general anesthetic for dentistry and, of course, that requires a specially trained anesthetist to be present throughout, as well as the surgeon dentist and several members of staff. It can be necessary to have between six and ten highly skilled medical professionals in the operation, depending on the case. And, of course, that's very expensive. The parents of many children simply don't have that kind of money.”
Croatian hospital Dr. fra Mato Nikolić in Nova Bila, which answered the call for free dentistry for all special needs children
A doctor of dentistry, Nikola Matković became acutely aware of the financial difficulties for many such parents in 2016, when NGO Betanija from Vitez put out a call for help. His main job is there, in the local health centre. They help provide care for about 50 special needs clients in the region. Responding to the call, Dr. Matković approached colleagues to see if they'd be interested in trying to help give free dentistry for all special needs children.
Dentist Lidija Lasić-Arapović and anaesthesiologist Zoran Karlović, both from Mostar, were quick to offer their assistance. They were followed by dentists Dr. Anja Hačimić, Dr. Ivana Dunđer-Vidović, Dr. Nikola Kezić, Dr. Ozrenka Raić from central Bosnia and assistants Slavica Šimić and Anita Martinović from Mostar. All agreed to join Dr. Matković in his attempt to offer free dentistry for all special needs children in their region.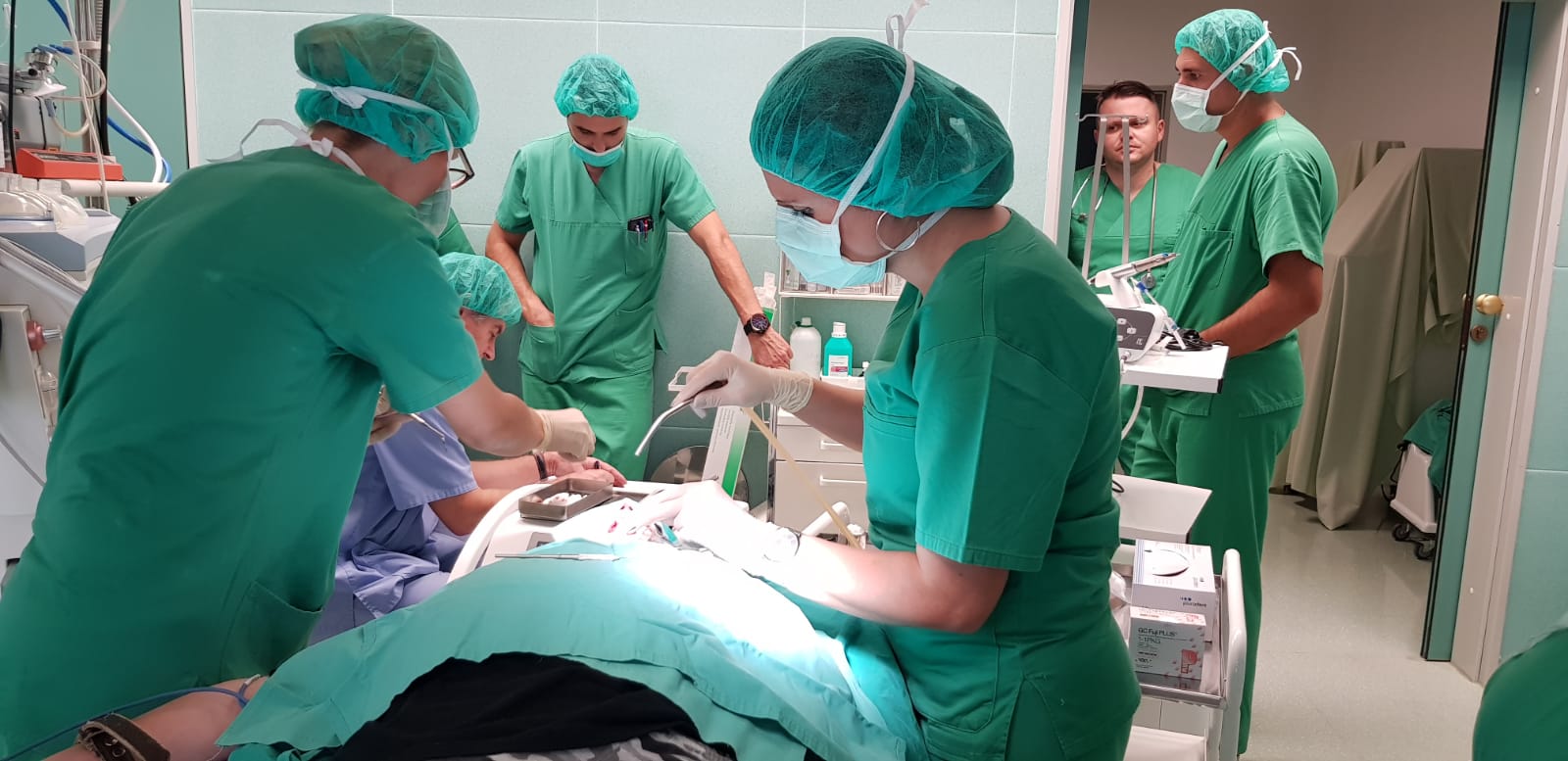
The team of Croatian hospital Dr. fra Mato Nikolić doctors at work, supplying free dentistry for all special needs children
Dr. Matković needed the approval of the Ministry of Health and of Central Bosnia Canton and authorities at the Croatian hospital Dr fra Mato Nikolić, lead by director Dr. Velimir Valjan, in order to begin the programme. Both quickly agreed that it was needed and agreed to contribute funding to help establish it. The programme of free dentistry for all special needs children in the Central Bosnia Canton region started in late 2018. But, that was just the beginning.
“We soon started getting calls from parents of special needs children from outside the region,” remembers Dr Matković. “And from full-time carers of adults who also have special needs. We soon realised we could not just leave them with nowhere to turn. We again approached the authorities and asked for permission to widen the programme and they were incredibly supportive. We've so far had around 120 clients, between the ages of six and thirty-five. And they've travelled here for treatment from every corner of Bosnia.”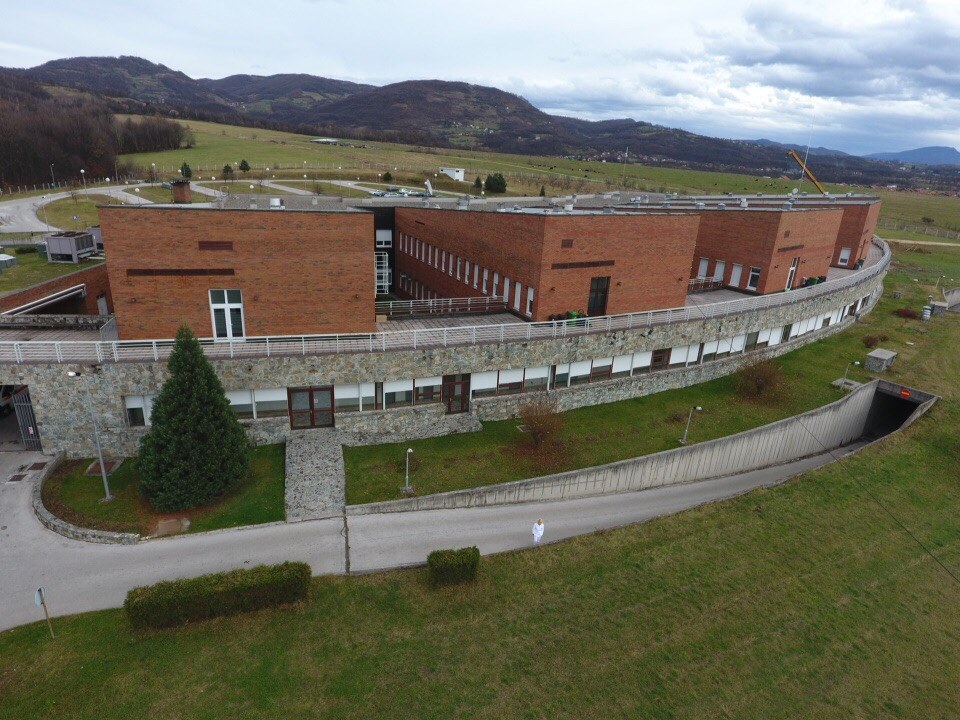
Croatian hospital Dr. fra Mato Nikolić. Welcoming all ethnicities and people of all religions, it gives free dentistry for all special needs children
For an outsider – such as this writer – if can be baffling to try and understand how Bosnia and Hercegovina works. The country is populated by the same people, although they've been separated for hundreds of years by three competing religions. This separation led to ethnic tensions rising during the break up of Yugoslavia, leading to Bosnia now being split up into several internal cantons under one federation, another autonomous state - Republika Srpska - plus the self-governing district of Brčko.
“This question may be stupid, but is healthcare the same in Bosnia as it is in Croatia?” asks this British member of the TCN team, rather naively. “Do you have the same option of health insurance to all the people who live there, no matter where they live? And, you're called Croatian hospital Dr fra Mato Nikolić. Does that mean that you treat only Croats? Do Muslims and Serbs have their own separate hospitals?”
Dr Nikola Matković
“Ahahaha, it's not such a stupid question really,” laughs Dr Matković. “Bosnia can be a confusing place. Well, the answer to your first question is no. It's not the same as in Croatia, it's a lot more complicated because there's a completely separate system for those who live in Republika Srpska. But, I'm pleased to say that we have overcome all the bureaucracy and difficulties to be able to treat patients from every part of Bosnia, including Republika Srpska. The NGO Betanija who set the ball rolling is a multi-ethnic organisation. They welcome people of every ethnicity and religion. So do the Croatian hospital Dr fra Mato Nikolić and this programme within it. Our hospital is called Croatian hospital because it was set up with great financial assistance from the Croatian government.”
The parish church of the Holy Spirit in Nova Bila became the only medical resource for some 70, 000 trapped people during the war. Around half of them were refugees.
Croatian hospital Dr fra Mato Nikolić is named after a prominent Bosnian Franciscan, humanist and the first graduate doctor from Bosnia and Herzegovina - Fr. Mato Nikolić (1776-1844). It is a hospital known throughout Bosnia and Croatia because of the heroic work undertaken there by staff and volunteers during the time of war.
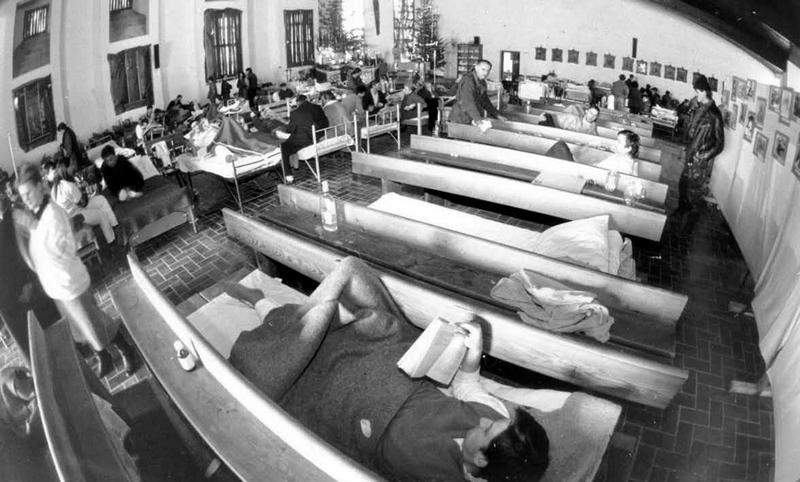

The church hospital in the time of war
In 1992, violent fighting caused a huge wave of forced migrations all across Bosnia. In the area where the hospital is now situated, the population almost doubled with the arrival of refugees. Some 70,000 people found themselves in an area 30 kilometers long and 2 kilometers wide. They were cut off from the rest of the world by the lines of fighting and by blockades. No hospital existed within the area, just the parish church of the Holy Spirit in Nova Bila. From there, a few healthcare professionals worked day and night, with almost no supplies, to treat the sick and wounded. So cut off was this group of people that they faced famine. The absence of any medical supplies was secondary to the very real threat of starvation.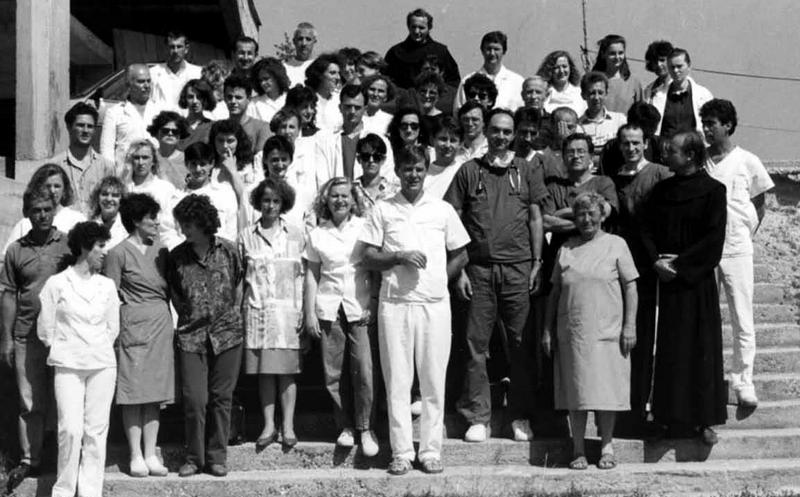
Staff of the war hospital Fr. Mato Nikolić pictured in 1993
War hospitals set up to try and deal with the trapped people proved ineffective, as the lines of fighting were constantly shifting. But, at the end of 1992, it was decided that the church in Nova Bila would be established as the main hospital for all those within the four municipalities of Travnik, Novi Travnik, Vitez and Busovača in the Lašva Valley. This war hospital took the name Fr. Mato Nikolić.
Despite having no regular supplies of electricity or even water, between 19 October 1992 to 1 April 1994, over 20, 000 people were treated and cared for in the hospital. 1,260 operations were performed under general anesthesia, 4,200 under local anesthesia. 721 children were born.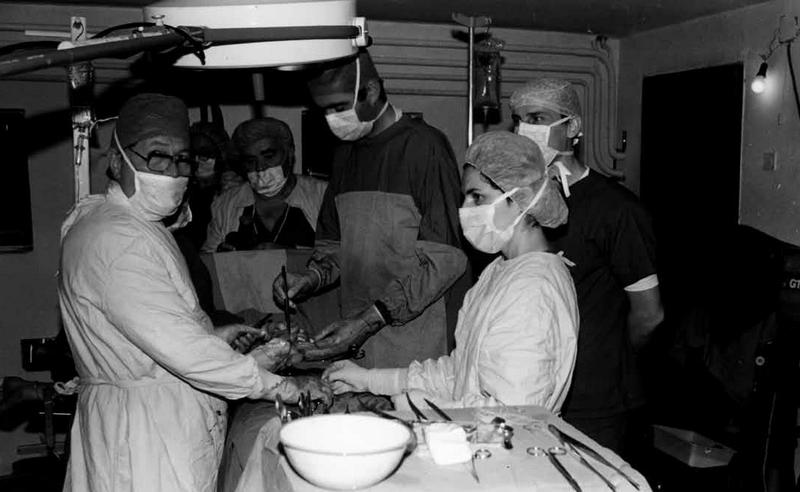
Despite having no regular supplies of electricity or even water, between October 1992 to April 1994, over 20, 000 people were treated and cared for in the hospital. 1,260 operations were performed under general anesthesia.
In June 1994, the President of the Republic of Croatia, Dr. Franjo Tuđman, visited the Lašva Valley and promised to build a new hospital. The new Croatian hospital Dr. fra Mato Nikolić was opened in 1999. Its pioneering programme to offer free dentistry for all special needs children from across Bosnia is just the latest commendable action undertaken by those associated with this hero hospital.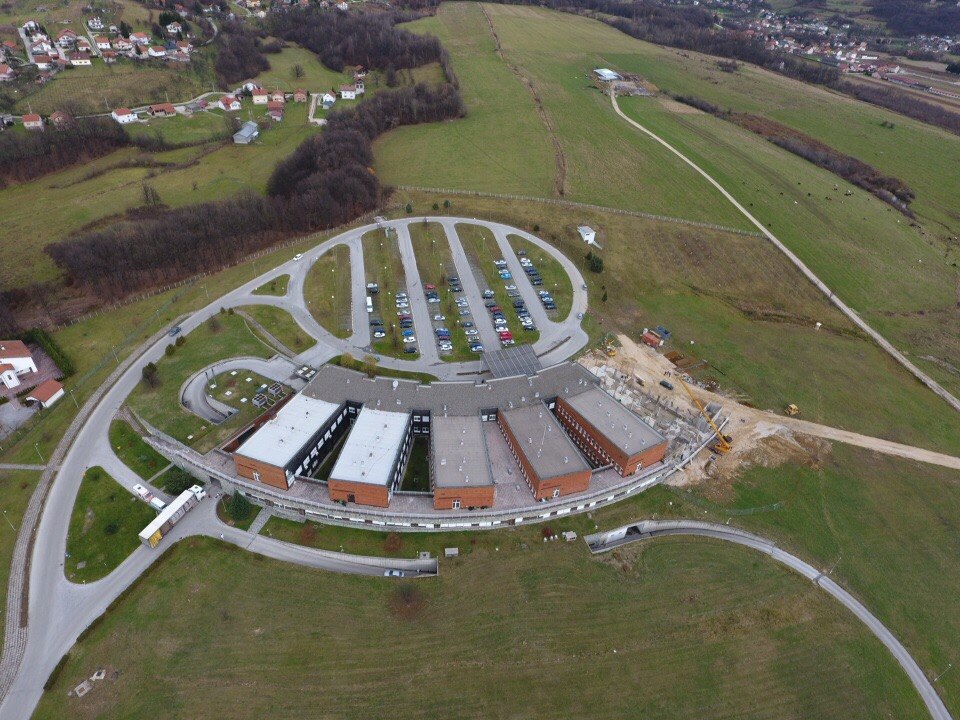
How the new Croatian hospital Dr. fra Mato Nikolić looked a few years ago, as its sixth wing was being constructed
All colour photographs © Croatian hospital Dr. fra Mato Nikolić, Dr Nikola Matković and municipality of Vitez
All black and white photographs © Bijeli Put documentary, original sources Davor Višnjić, Željko Maganjić, Srećko Stipović, Arhiv konvoja Bijeli put, Arhiv Kruh svetog Ante, Foto klub Split
For the latest travel info, bookmark our main travel info article, which is updated daily.
Read the Croatian Travel Update in your language - now available in 24 languages
Number Of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients In Croatia Up 110% - Newspaper
ZAGREB, Sept 5 (Hina) - The number of hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Croatia has increased by as much as 110% in the past 15 days, Jutarnji List daily said on Saturday, adding that the growing number of severe cases is worrying.
Although the actual figures do not seem so terrifying, because 135 people were receiving hospital treatment for COVID-19 on August 21, while their number on September 4 was 283, the trend is a serious cause for concern, the newspaper said.
The number of active cases in this period jumped by 47%, which is more than half the increase in the number of hospitalized patients, as the number of active cases rose from 1,841 on August 21 to 2,703 on September 4.
A further cause for concern is the fact that the share of hospitalized COVID-19 patients in Croatia in the total number of infected people was 7.33% on August 21, while on September 4 it was 10.5%, Jutarnji List said, adding that the number of deaths in the said period rose from 169 to 195.
These figures are not surprising given that Croatia has been seeing negative trends for days now, and it was only logical that this situation would also affect the hospitals, which were not under too much strain this summer despite the constant presence of the virus. This was mostly due to the fact that symptoms of the disease were milder than those seen during the first wave of the epidemic from March to June, and the fact that people spent much more time outdoors, Jutarnji List said.
For the latest travel info, bookmark our main travel info article, which is updated daily.
Read the Croatian Travel Update in your language - now available in 24 languages
Zagreb Children's Hospital Gets Therapy Dog
September 3, 2020 – A Zagreb Children's Hospital is preparing to welcome its first canine member of staff – Jupi, a border collie
They are often said to be the most intelligent of all dogs. Used traditionally for herding livestock, border collies can learn a very large number of signals and commands. They are eminently trainable. Now, that intelligence is to be applied to the area of therapy, as one Zagreb children's hospital prepares to welcome its first border collie as a member of the team.
Still only a puppy, Jupi is being prepared for the role by her owner, Iva Zečević, a clinical psychologist at the Psychiatric Hospital for Children and Adolescents. At the moment, Jupi still needs to get her jabs, go for training and pass a therapy dog exam, Iva revealed to Jutarnji List journalist Lada Novak Starčević in a recent interview.
Border collies are very intelligent and eminently trainable. They take their name from the sheep farming lands which are situated on both sides of the Anglo-Scottish border © Yuppy Ermeton
Iva is undertaking the training herself with help from puppy coach Ana Odak and The Croatian Association for the Training of Guide Dogs and Mobility. Iva decided to dedicate herself personally to the task because she knows the Zagreb Children's Hospital where she works would struggle to pay for a fully trained therapy dog. Despite the time and costs involved in the necessary process, Iva has previously seen the positive effects dogs can have on her patients and knows it's a worthwhile undertaking. She is an experienced dog owner and has kept and trained several, although this is the first she has trained as a therapy dog.
Border collies are so clever that they thrive best in households that can give them lots of play and exercise. It is a British breed of dog, taking its name from the sheep farming lands which are situated on both sides of the Anglo-Scottish border. The word collie comes from the old Celtic word for useful.
All of today's purebred border collies can trace an ancestral line back to one dog. Old Hemp lived in Northumberland between 1893 and 1901 and was so skilled in his work with sheep, as well as having exactly the right temperament, that many shepherds used him as a stud for their future working dogs. Old Hemp is believed to have sired as many as 200 puppies to be reared as sheepdogs.
For the latest travel info, bookmark our main travel info article, which is updated daily.
Read the Croatian Travel Update in your language - now available in 24 languages
Minister: Expert Group Allows Parents To Visit Their Hospitalised Children
ZAGREB, July 1, 2020 - Health Minister Vili Beros said on Wednesday that an expert group had unanimously decided to make it possible for parents whose children were hospitalised to spend with them 15 minutes a day and that a recommendation to that effect would be sent to all hospitals caring for children.
"A unanimous decision has been made that, despite the epidemic, it is of great importance to enable parents to be with their child who is undergoing hospital treatment, notably regarding the age (children under the age of three) and the duration of treatment (long hospital stay)," Beros wrote on his Facebook wall.
The Health Ministry will send a recommendation to all hospitals caring for children to enable parents to stay with their child when that is possible considering available space, namely regular visits on the condition of compliance with epidemiological measures, the minister said.
The Roda parents' association earlier in the day said it had gathered more than 35,000 signatures of parents for a petition asking the Health Ministry to cancel the current ban on parents' visits to and stay with their children undergoing treatment in hospital, a restriction introduced to help contain the spreading of the coronavirus.
From Lovran to Zagreb: How Do Croatia's Hospitals Stand Financially?
As Novac/Frenki Lausic writes on the 4th of May, 2019, across 59 hospitals in Croatia, a total of 41,692 workers are employed, out of a total of 65,000 employees in the health care system, and the share of health workers in the total number of hospitals ranges from 70.1 percent in the Lovran Orthopedic Clinic, to 81.2 percent at the Clinical Hospital Centre in Zagreb.
From this data, it could easily be concluded that the hospital in Lovran operates poorly, as it has a large number of administrative staff who aren't directly involved in the care of patients, while KBC Zagreb is best placed financially because it has the least employees in administration. The reality is exactly the opposite: Lovran is the best Croatian medical institution financially, making it one of the ten major state hospitals operating without any losses, while KBC Zagreb has the biggest losses, the most obligations, and the most outstanding unpaid obligations.
However, data on the positive financial performance of hospitals may be correlated with the fact that the largest share of beds (in total capacity) is boasted by the clinic in Lovran, 82.61 percent, while OB Varaždin, one of the general hospitals with the worst business indicators, has the largest number of beds for long-term and chronic treatment, as well as palliative care (511 beds, or 49.18 percent of the total bed capacity of the hospital) due to the merging of the Novi Marof Hospital for Chronic Disease and the Hospital for Lung Diseases, and TBC Klenovnik OB Varaždin.
Therefore, the status and causes of success and failure in Croatia's hospitals need not be judged at first impression because each hospital is a special case for itself and requires a deeper analysis. However, there are also common denominators when it comes to the ''bad'' side of the Croatian hospital system, ranging from poor financial results, some bad patient outcomes, long waiting lists, and some institutions with literally horrible sanitation facilities.
In response to a survey conducted by Maja Vehovec, Ivana Rašić Bakarić and Sunčana Slijepčević, researchers from the Economics Institute back in 2012, which included one director of the Clinical Hospital Centre, three directors of general hospitals and two directors of special hospitals and representatives of the association of employers in the health system, it can be seen that when finances are in question, "the root cause of the problem with not paying costs is seen by directors as a continuous imbalance between the revenue received and the expense accounted for."
The basic part of the hospital's income is, in fact, the income that the hospital receives from HZZO, which are presented as the so-called "limits", ie, the annual budget funding which was introduced back in 1997.
For this reason, the authors point out that the limits to be allocated to hospitals should be based on objective indicators such as the number and types of surgeries, the number and type of outpatient examinations and the like, ie, the costs of each activity. The second management model in this part, based on the payment of the services provided, began being implemented back in 2015, at the time when Croatia was ruled by an SDP government, but such a practice was later stopped by the HDZ government, which returned the "limits" method the following year.
The Croatian Government and the Ministry of Health have decided to ''repair'' the situation this year by increasing their contributions to the healthcare system from 15 to 16.5 percent.
Make sure to follow our dedicated lifestyle page for more information on Croatia's healthcare system, hospitals in Croatia, the quality of treatment in Croatia and much more.
Click here for the original article by Frenki Lausic for Novac/Jutarnji


