Friends of Croatia: Diplomatic Immunity
June 3, 2021 - The seventh article in the series, Friends of Croatia: Diplomatic Immunity brings you more details on diplomatic immunity, its boundaries, and examples of exceptions in accordance with the International Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations. Details on how the sentry Ministry of Foreign and European Affairs, are included too.
Being a diplomat isn't bad at all. You get to travel and explore the country you are assigned to, experience the new culture while promoting your own. Additionally, you work on improving bilateral relationships and contributing to the dynamic of the geopolitical scene (hopefully for the better).
Earlier in the series, there was an article dedicated to the key terms of diplomacy. But, there is one more thing that is worth giving special attention to: diplomatic immunity.
You probably might be thinking that means exemption from legal prosecution, and you are kinda right. But that doesn't just mean you can just do whatever you want, and law-abiding behavior is, of course, one of the needed characteristics to fit the job description.
In fact, the International Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations from 1961 has very clear instructions.
„The person of a diplomatic agent shall be inviolable. He shall not be liable to any form of arrest or detention. The receiving State (a State in which the diplomat is based) shall treat him with due respect and shall take all appropriate steps to prevent any attack on his person, freedom or dignity“, says article 29 of the Vienna convention. Its also worth adding that the same protection applies for his/her private residence, as well as papers and correspondence, and the diplomatic agent is also not obliged to give evidence as a witness.
But, for not everything to be all benefits and no responsibilities, article 31, despite repeating that „ a diplomatic agent shall enjoy immunity from the criminal jurisdiction of the receiving State and that diplomatic agent „shall also enjoy immunity from its civil and administrative jurisdiction“ – he lists exception. Such as in the event of a real action relating to private immovable property situated in the territory of the receiving State, (unless he holds it on behalf of the sending State for the purposes of the mission) or in the case of an action relating to succession in which the diplomatic agent is involved as executor, administrator, heir or legatee as a private person and not on behalf of the sending State and finally, in the event of an action relating to any professional or commercial activity exercised by the diplomatic agent in the receiving State outside his official functions.
Additionally, „the immunity of a diplomatic agent from the jurisdiction of the receiving State does not exempt him from the jurisdiction of the sending State“.
Ministry at your (diplomatic) service
With the Croatian Ministry of Foreign and European Affairs already stating for this series that they take diplomatic relations very seriously, they respect the convention, and their Diplomatic Protocol Office is here to help. As evident in their protocolar guide, they have an entire section dedicated to privilege and immunity.
„Diplomatic missions and international organizations accredited in the Republic of Croatia notify the Ministry of Foreign and European Affairs, to the Diplomatic protocol arrival of the (diplomatic) mission, attaching the diplomatic note, and the copy of the passport that will be notified“, states the guide in respects to the International Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations. The guide adds that when stepping on duty, the Diplomatic protocol will have a view in the passport of a notified person, and it will place a stamp with the following content that will confirm the passport was reviewed by the Ministry. Along with the date and signature to match. This leads to issuing a special identity card that then allows entering the Republic of Croatia without a visa.
„The special ID is issued to the members of missions and consulate offices, members of the UN organizations, and other specialized UN institutions, members of international organizations accredited in the Republic of Croatia, as well as members of their families or members of the shared household and members of private service“, elaborated the guide.
With the aforementioned documents, to get the ID, diplomats must also provide their photos and fill in a questionnaire which can be downloaded from the guide.
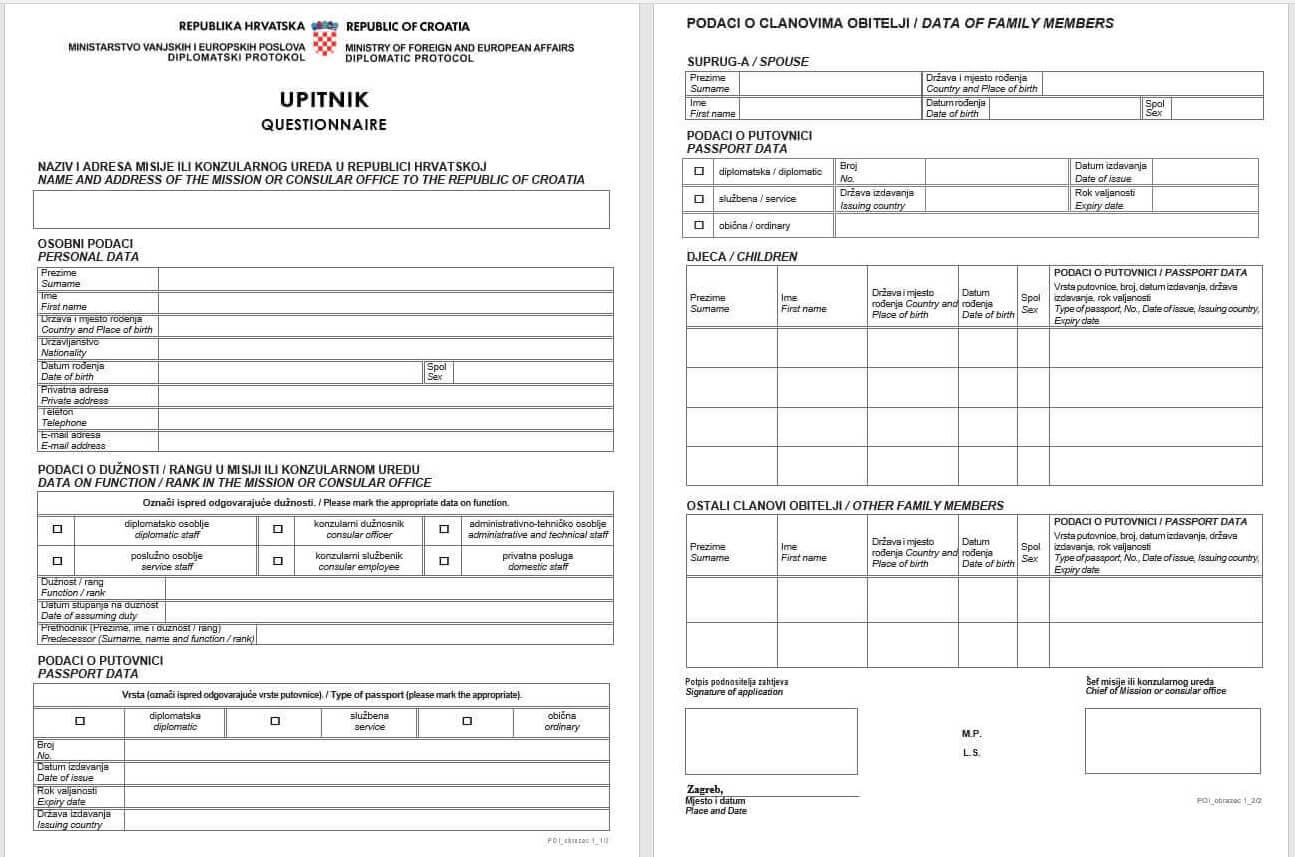
Diplomatic protocol questionnaire/screenshot, Total Croatia News
To read more from the series "Friends of Croatia", follow TCN's dedicated page.
For more about diplomacy in Croatia, follow TCN's dedicated page.
Friends of Croatia: Basic Terms of Diplomacy
April 29, 2021 - The second article in the series "Friends of Croatia" covering all things diplomatic, looks into an overview of the basic terms of diplomacy both for a more accessible following of the series,as well as for safer travel and for being more informed in general.
When exploring Croatian diplomatic relations, terms such as diplomats, embassies, ambassadors, and consulates are the keywords of the topic. Diplomacy is important of course for countries to communicate, express and arrange mutual cooperation, push their respective interests, and offer help to their citizens in another country. But, what is for what and who is for who?
The embassy is for everything, the consuls are for more minor details
As Postoffice.uk points out, to a fellow traveller these questions may not be of too much importance, but having a bit of trivia knowledge never hurts.
''An embassy is the base for a country’s diplomatic mission abroad – meaning all of the political, cultural and social relationships between the two countries. There will only be one embassy for one nation in another country, as it is where the country’s ambassador works (and sometimes resides). A consulate is where consular services are performed. Embassies will normally have a consular section. While there will be only one British Embassy in the country you visit, there may be a number of consulates. These would usually be in cities with the most tourists,'' writes Postoffice.uk.
It's worth noting that while the aforementioned explanation is written from the British perspective, this difference is appliable to any country.
The Thought.com page illustrates that very well, explaining the difference in the case of the United States of America.
''An embassy is responsible for representing the home country, for handling major diplomatic issues (such as negotiations), and for preserving the rights of its citizens abroad. Consulates (and their chief diplomat, the consul) handle minor diplomatic issues such as issuing visas, aiding in trade relationships, and taking care of migrants, tourists, and expatriates,'' writes Thought.com. The site adds that usually when a country recognises another as being sovereign, an embassy is established to maintain foreign relations and provide assistance to travelling citizens.
Embassies and consulates can help a person out with many things. For instance, if you lose your passport, the diplomatic representatives can acquire you a new one. If you get sick, they can offer you the contacts of local doctors or lawyers in case you're the victim of a crime.
They can't offer you healthcare which is of a different level than the one there is in the country already, nor can they lead any sort of investigation themselves; they can't even pay you money or offer remuneration, but the contacts they can provide as well as the advice they can give can help you tremendously when coming unstuck in a foreign country.
This is why its important to be informed where the embassies or consuls of your country are located in the country you're visiting. But, don't expected them to help you if you end up in trouble with the law in another country yourself, as they can't interfere in those legal processes in respect of other nation's sovereignty. Despite that, they can give you lists of lawyers and guides to the legal process in the country you're visiting, visit you if you're arrested, and maintain contact with your family to inform them of what happened. While you hopefully won't end up in a dire situation it is still better to travel while being as informed as possible. Usually, a bit of common sense and decency will let you avoid such incidents.
Your country is a host to the embassies of other countries too, and you can visit them if you want to travel to another country to check your visa requirements. Keep in mind that in embassies, the country where the embassy is located doesn't have jurisdiction in the embassy, and you can be arrested in the embassy by security forces or ask for protection to avoid arrest from the forces of the country the embassy is in. The ever-controversial Julian Assange finding refuge in the Ecuadorian embassy in London to avoid arrest is perhaps the best-known example of this, and he was arrested by the British police only after negotiations with Ecuador were conducted.

pixabay
Ambassador and diplomat: the same job, but the ambassador is the boss
Similar to all toes are fingers, but not all fingers are toes – the ambassador is the highest-ranked of all diplomats in the embassy.
''The ambassador is the highest official in the embassy and acts as the chief diplomat and spokesperson for that embassy's home government. Ambassadors are typically appointed by the highest level of the home government. In the United States, ambassadors are appointed by the president and confirmed by the Senate'' writes Thought.com.
As Wikidiff compares it, the ambassador is ''a minister of the highest rank sent to a foreign court to represent his sovereign or country there. (Sometimes called ambassador-in-residence )'' or ''an official messenger and representative''. A diplomat, in essence, is, as Wikidiff continues: ''A person who is accredited, such as an ambassador, to officially represent a government in its relations with other governments or international organisations.''
Marc Finaud, the Head of Arms Proliferation at Geneva Centre for Security Policy (an international foundation for promoting the building and maintenance of peace, security, and stability), writes that diplomats have five main tasks in accordance with the international Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations from 1961. ''Representation, protection of national interests, negotiations, reporting, and the promotion of friendly relations. Such skills can also be of interest for non-diplomats engaged in professional activities involving contacts with foreign people or cultures,'' writes Marc Finaud for GCSP.
Diplomacy is interesting, challenging, and above all, an important profession, and much more can be written about it than just this text. Still, these are the basic facts of diplomacy to follow in this series and to arrange safer and more informed travel abroad.
To read more from the series "Friends of Croatia", follow TCN's dedicated page.
For more about politics in Croatia, follow TCN's dedicated page.


